Geneva Covid-19 study: undetected cases, but too few for herd immunity
Initial results from a serological antibody test in canton Geneva has estimated that over 5% of the Geneva population – some 27,000 people – could have been infected by the novel coronavirus. That is more cases than counted by officials, but fewer than researchers had hoped for to achieve immunity.
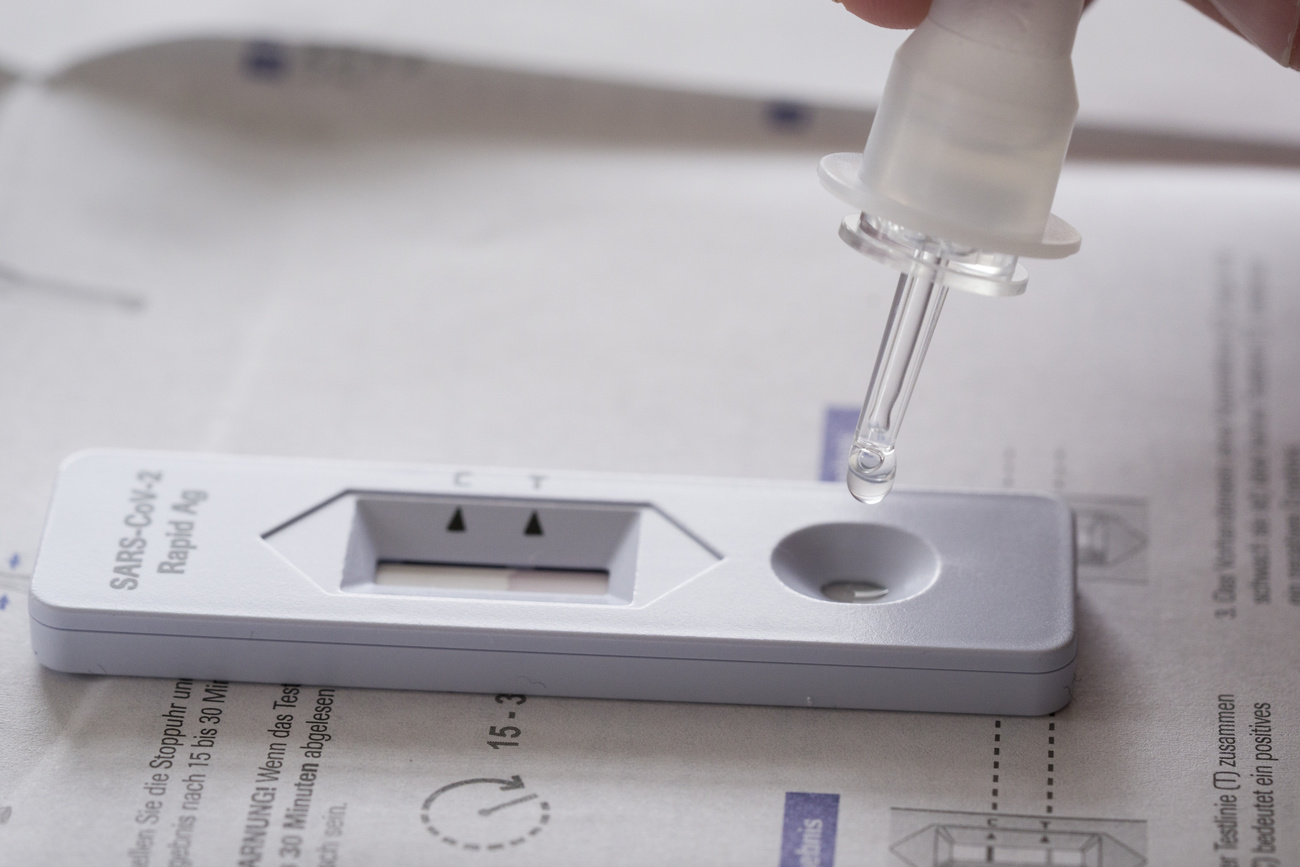
The studyExternal link released by the Geneva University Hospital on Wednesday is based on blood samples taken from 760 people in Geneva. Serological tests were used to detect a specific antibody type G, which is directed against the pathogen. The test confirms the presence of antibodies in the blood, but researchers caution that this does not indicate whether someone has any immunity against the virus.
Based on the sample, the researchers estimate that the seroprevalence in the population to be 5.5% on April 17, 2020, which means that 27,000 people would have been exposed to the coronavirus. This is much higher than the official government estimates for canton Geneva, which is around 4,900 confirmed cases on Thursday. Geneva has been one of the hardest-hit cantons in Switzerland.
The fact that the actual number of infected people was far higher than the official positive test was expected given testing for the virus (not the antibodies) has largely focused on people displaying symptoms or at high risk of serious illness.
Some experts say, however, that this is still far off from what they had hoped in order to achieve “herd immunity” whereby a significant portion of the population (upwards of 70%) are immune to infection.
“What is already emerging is that the proportion of infected people is smaller than hoped for,” Isabella Eckerle, virologist at Geneva University Hospital, told Swiss public television SRFExternal link.
In a press release, the hospital stated that the results of the study indicate that the serological test platform at the hospital reliably confirms exposure to Covid-19 twenty days after the onset of symptoms.
Swiss pharmaceutical company Roche announced that it will be launching its own antibody test in May. In an interview in Reuters on Wednesday, CEO Severin SchwanExternal link warned that some of the current tests marketed to tell people if they have been infected, are a “disaster”. He told reporters, “these tests are not worth anything or have very little use”.
Large-scale study
On Thursday, the Swiss School of Public HealthExternal link – a consortium of 12 universities – announced the launch of a nationwide study to assess the proportion of the Swiss population with antibodies against the new coronavirus. The study called “Corona Immunitas” is a public-private partnership supported by the Federal Office of Public health, private companies, and individual experts.
The study, which is scheduled to run for six months, will invite 25,000 residents in Switzerland to participate in antibody blood tests. This is intended to provide reliable data on the number of antibody carriers in different regions and in specific population groups, as well as on the extent and duration of immunity against Covid-19.

More
Coronavirus: the situation in Switzerland

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative




















You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.