
Switzerland signs international space agreement
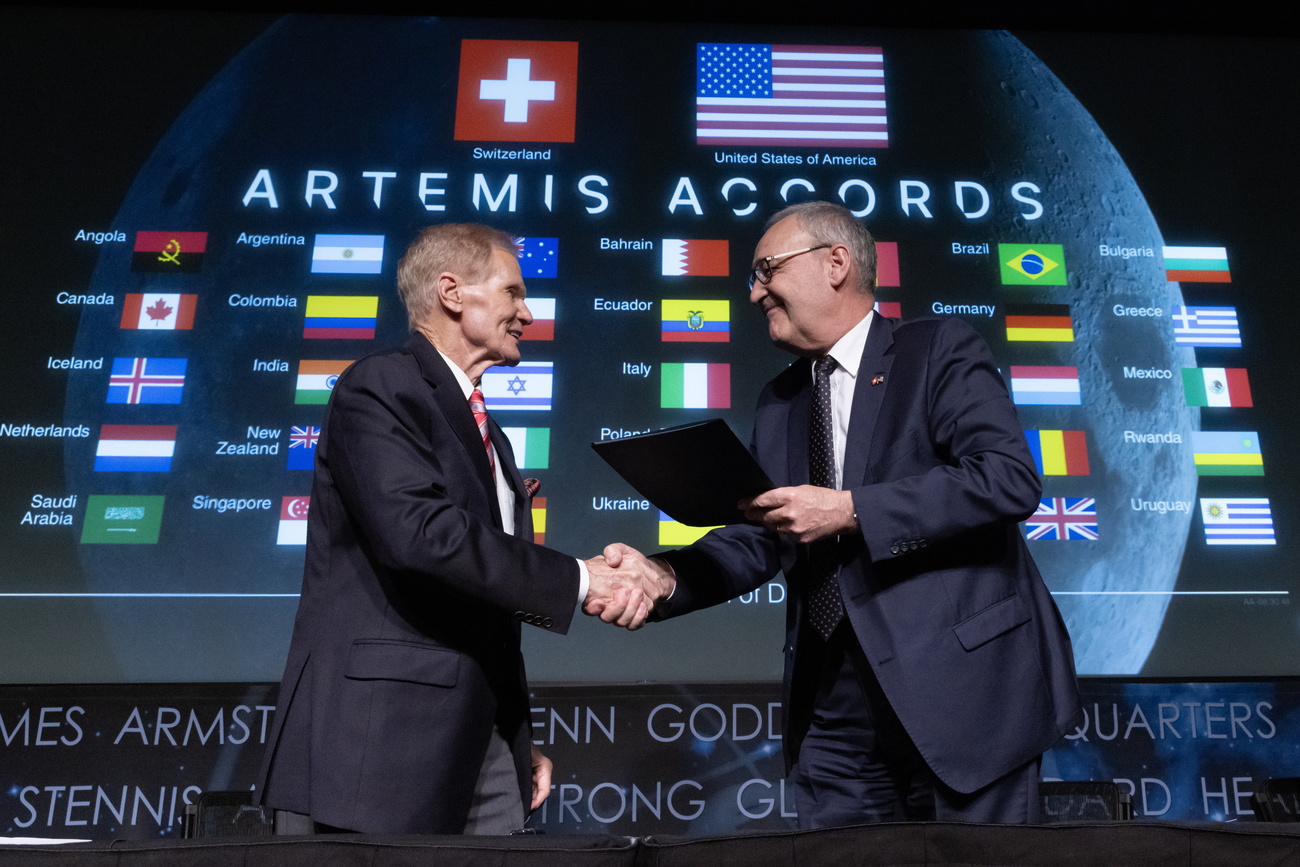
Swiss Economics Minister Guy Parmelin signed the Artemis Accords at NASA's headquarters in the US capital of Washington D.C. on Monday.
As a result, Switzerland has agreed to promote the peaceful exploration of outer space with the US and 35 other signatories.
Bill Nelson, administrator of the US space agency NASA, described the signing as a “a giant leap forward in the partnership” between Switzerland and the US.
Former NASA astronauts have not only travelled with outstanding Swiss experiments, said Nelson, but also with an outstanding Swiss colleague: Claude Nicollier, the first Swiss astronaut, has flown on the space shuttle four times.
Parmelin pointed out that there is now another Swiss among the Artemis astronauts: 35-year-old Marco Sieber. It is not yet clear when and if Sieber will set foot on the moon. Sieber told Keystone-SDA news agency in Washington D.C. on Monday that a six-month mission on the International Space Station (ISS) was probably first on his itinerary.
+Swiss astronaut Marco Sieber: ‘Money for space travel is an investment’
Sustainable presence on the moon
The Artemis Accords are intended to play a key role in achieving a sustainable and robust presence on the moon before the end of this decade, and at the same time prepare for a historic manned mission to Mars. However, Sieber doubted that his generation of astronauts would fly to Mars.
Together with seven other countries, the US signed the Artemis Accords in 2020. As numerous countries and private companies carry out missions and operations around the moon, common principles are required for the civilian exploration and utilisation of space.
+Switzerland unveils 2023 space strategy
Switzerland is the 37th nation to sign the non-binding treaty. Space-travelling nations China and Russia are not members of the agreement, which was drawn up in coordination with the UN Outer Space Treaty.
NASA representative Nelson said that the agreement ensured that the future belongs to countries that explore the cosmos openly, safely and in peace.
+In space exploration, Switzerland punches above its weight
Switzerland ‘has a lot to offer’ in space
At the signing, Parmelin said that Switzerland had a lot to offer in the realm of space travel: excellent scientists, highly innovative and competitive companies, a new space policy, and soon the first space law.
+ETH Zurich to offer new degree in space science
The US and Switzerland have a long history of successful cooperation in the space sector. One of the first scientific experiments of the Apollo 11 moon mission was a solar wind sail from the University of Bern. Both countries are also participating states in the ISS.
Translated from German by DeepL/kp/amva
This news story has been written and carefully fact-checked by an external editorial team. At SWI swissinfo.ch we select the most relevant news for an international audience and use automatic translation tools such as DeepL to translate it into English. Providing you with automatically translated news gives us the time to write more in-depth articles.
If you want to know more about how we work, have a look here, and if you have feedback on this news story please write to english@swissinfo.ch.

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative

























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.